
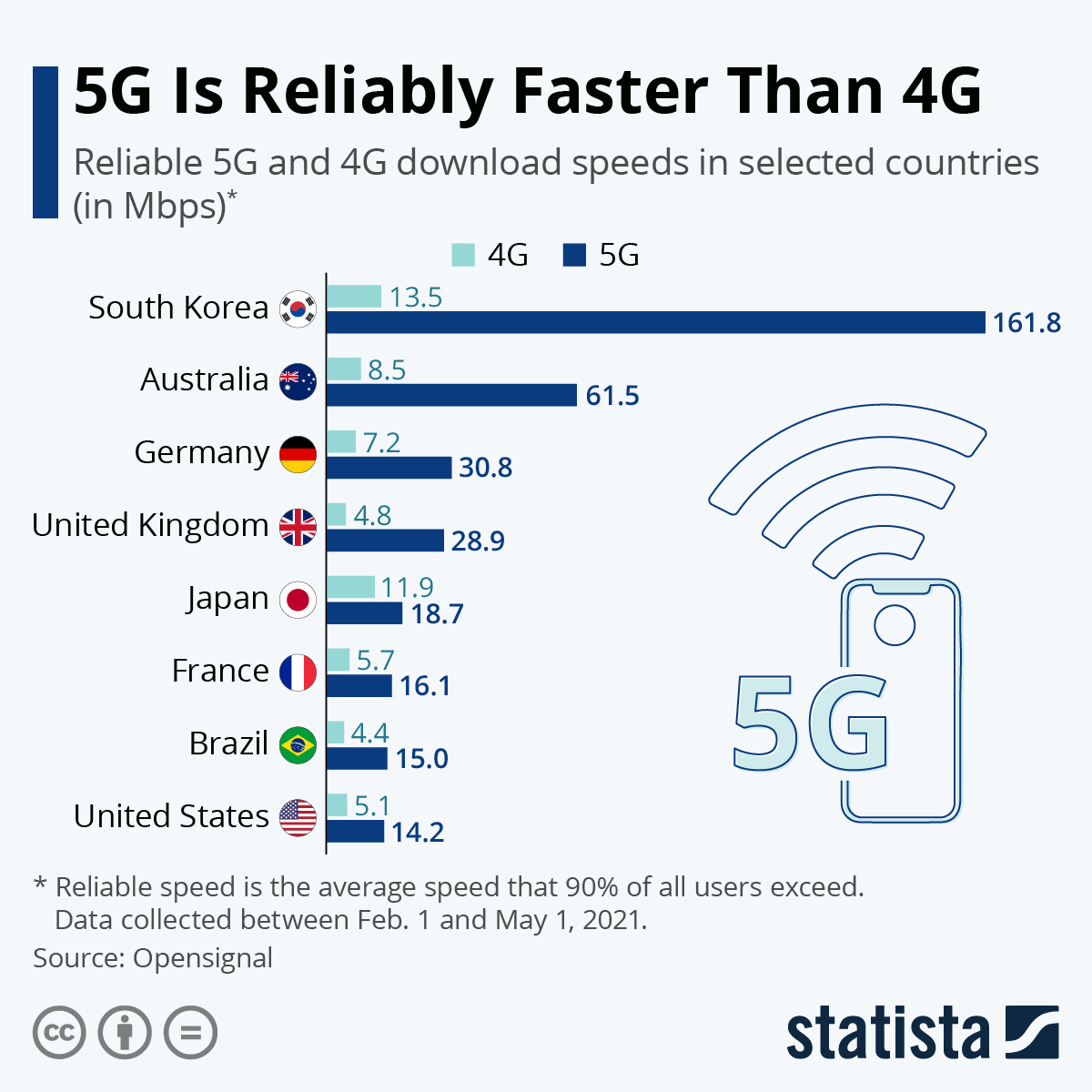
At the moment, the main benefit most users may see is faster downloads of large files like movies. You may notice this in the form of 5G antennas popping up in your city, often on existing utility poles.Ĭoverage for these mmWave networks remains fairly limited. The downside of these channels is that they have a very short range, requiring many smaller cell sites.

These radio frequencies are known as ultra-capacity or millimeter-wave (mmWave) channels. The faster 5G signals use higher radio frequencies. This makes them ideal for crowded areas that require more bandwidth like college campuses, stadiums, and even apartment buildingsĤG networks often get crippled in these heavy-use areas, but 5G offers a lot more breathing room and won’t slow down under load. This can result in a smoother gaming experience and improved real-time control of drones and driverless vehicle communication.ĥG networks can support many devices at once. 5G offers latency under 5 milliseconds, whereas 4G offers between 60 and 98 milliseconds.Īlthough web browsing may not feel hugely different on 5G versus 4G, it can have a significant impact on applications where response time matters. Latency is the time it takes for data to travel between two points. However, as carriers build out the infrastructure and turn on new channels, real-world speeds will continue to increase.ĥG also offers drastically reduced latency compared with 4G. 5G gets this speed from its ability to use a wider range of radio frequency channels, but wireless carriers have to make those channels available for it to have any impact.įor this reason, 5G might not seem any faster for some customers. What 5G brings to the table is the ability to operate on a much wider range of channels and frequencies than past generations of wireless tech.Ĭompared with the previous 4G network, 5G technology brings three main benefits: faster speed, increased responsiveness, and improved ability to handle network traffic.ĥG speeds can reach up to 20 Gbps - at least in theory. As with other networks, it’s broadcast from cell sites, such as towers.
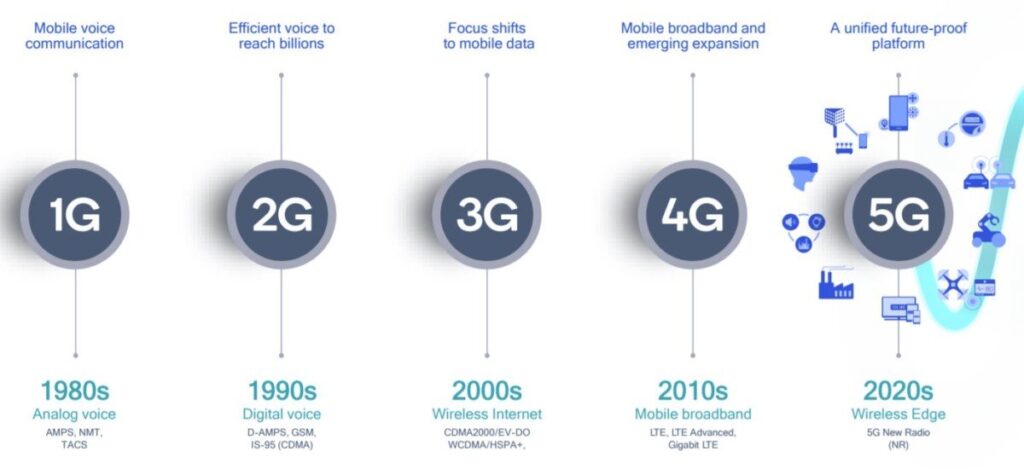
How does 5G work?ĥG is the fifth generation of mobile network technology. Latency measures the time it takes to move a unit of data from one location to another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
